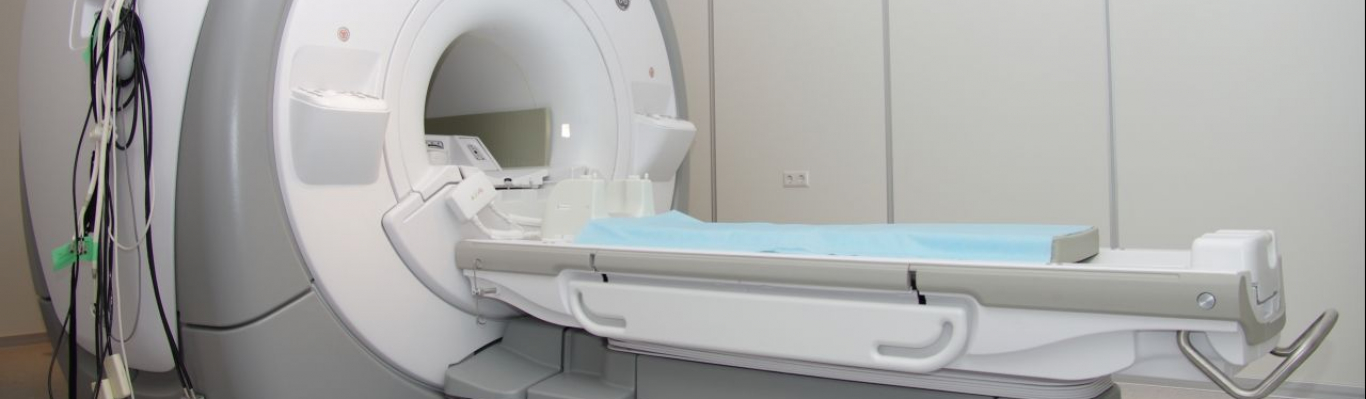
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Therefore, magnetic resonance imaging is a complex, but safe and effective diagnostic method. This method does not involve ionizing radiation. This method reveals various pathological processes in the study of the brain and spinal cord, spinal column, small pelvis, kidneys, adrenal glands, knee joints, soft tissues and other organs.
This method was originally called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging, but in the late 1970s, due to negative associations with the word "nuclear", it was renamed magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and a spectroscopic technique used by scientists to obtain data on the chemical and physical properties of molecules. MRI uses tomographic imaging to image the NMR signal from thin slices passing through the human body. In the future, MRI develops from a tomographic imaging method to a volumetric (3D) imaging method.
What is the MRI?
The method of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the property of protons that make up a water molecule to change their “behavior” in a magnetic field. Scanning can be performed in three mutually perpendicular planes with an arbitrary, in contrast to computed tomography, tilt angle without changing the position of the patient in the lumen of the magnet. Special techniques for processing the combined response RF signals make it possible to obtain an image of the patient's internal organs in three-dimensional space.
MRI is more often used to diagnose damage, tumor formations of the nervous system, as well as in oncology, when it is necessary to determine the presence and extent of the tumor process. The list of diseases that can be detected using MRI is quite impressive: inflammatory, dystrophic and tumor lesions of blood vessels and heart, organs of the chest and abdominal cavity, damage to lymph nodes, parasitic processes and other pathologies.
Currently, nothing is known about the harm of a magnetic field. However, most scientists believe that in conditions where there is no data on its complete safety, such studies should not be subjected to pregnant women.
Due to its high information content, MRI tomography is usually prescribed in cases of controversial diagnosis or ineffectiveness of other research methods. But MRI cannot be performed on those people whose bodies contain various ferromagnetic (magnetic) metal structures and medical electronics - artificial joints, heart pacemakers, defibrillators, various orthopedic structures.
Preparation to MRI
For most MRI examinations, no special training is required, only 2 types of examinations require specific training:
MRI of the abdomen - it is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking for 5 hours before the examination. This is necessary to keep the gallbladder full.
MRI of the pelvic organs - the bladder must be full. In 60 minutes before the study, you must drink 1 liter. water for better visualization of the urinary tract.
For women, for the greatest information content of the study, MRI of the mammary glands must be performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (from 7 to 12 days, it is necessary to count from the first day of the last menstruation), and during menopause and postmenstrual period - at any time.
While waiting in line for an MRI scan, we recommend that you do the following:
put all metal and electronic devices out of pockets;
- phones;
- players;
- flash cards;
- coins;
- magnetic cards (credit cards, contactless public transport cards, etc.).
remove from yourself:
- decorations, incl. earrings and piercings;
- watch and belt;
- removable dentures (when examining the head and neck).
This is necessary so that electronic devices and magnetic cards introduced into the magnetic field of the MRI scanner are not damaged.
What reminds the MRI procedure?
- The patient is placed on a pull-out couch
- The table is moved inside the tomograph
- The main condition is to lie still, as your movements can distort the results of the MRI
- During the procedure, the doctor is outside the MRI room
- But! The patient has the opportunity to contact the doctor if discomfort occurs
- Research usually lasts from 15 to 90 minutes
Getting an MRI scan can be difficult if you have noticed signs of claustrophobia or if you know you are afraid of confined spaces.
MRI types
Main types of MRI:
-
MRI of the brain, pituitary gland, angiography of cerebral vessels;
MRI of the brain and its vessels is used for:
- confirmation or exclusion of the diagnosis;
- the use of the results obtained and the appointment of the correct treatment, if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, cerebral vessels, and the neck area is by far the most effective and detailed method for diagnosing vascular diseases.
Indications for MRI of the brain:
- frequent headaches with special frequency;
- previously identified brain tumors or suspicions of their development;
- examination before brain surgery;
- identification of epileptogenic zones in the brain;
- stroke and control of the condition after it;
- frequent loss of consciousness for no apparent reason, fainting;
- inflammatory diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- degenerative changes;
- disorders of blood flow in the brain;
- monitoring the state of the tumor focus after treatment;
- inability to conduct computed tomography.
The pituitary gland synthesizes hormones that affect human metabolic processes, growth and reproduction. This gland is the central organ of the endocrine system. The pituitary gland is in close interaction with the hypothalamus. The study is used to identify cysts, adenomas, hormonal disorders and pathologies of the endocrine glands.
-
MRI of soft tissues of the neck, angiography of the vessels of the neck;
Timely MRI of the cervical spine makes it possible to detect circulatory disorders of this important area, which is responsible for the blood flow to the brain.
The main indications for MRI of the vessels of the neck and soft tissues:
- recurrent headaches;
- suspicion of the development of cervical osteochondrosis, pinching of nerve endings and impaired blood flow;
- dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- tendency to increase blood pressure without established arterial hypertension;
- decreased sensitivity of the fingers, tingling and numbness;
- spinal injury.
With the above complaints, it is recommended to consult a neurologist and conduct a neck examination. This will avoid further development of the disease and prevent complications.
-
MRI of the cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral spine;
When performing magnetic resonance imaging of the back, the following departments can be examined:
Cervical department. When performing MRI of the cervical spine, it is possible to detect intervertebral hernias, protrusions, instability of the vertebrae, bone outgrowths (osteophytes) and any deforming changes in the bone structures.
Chest section. If the patient was prescribed an MRI of the thoracic spine, then this procedure will provide information about the presence of hernial structures and protrusions, fractures and displacements, osteochondrosis, venous and vascular anomalies, pathological changes in the spinal cord.
Lumbar region. The MRI procedure of the lumbar spine is performed more often compared to the examination of other regions. Along with the examination of the lumbar spine, MRI of the sacral spine is performed, since both zones have combined functions in the body.
MRI of the sacral spine is most often prescribed by a neurologist in the presence of complaints of lower back pain and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
The study allows to identify degenerative-dystrophic changes in the tissues of the spinal column. Also, using MRI of the lumbosacral region with contrast, various neoplasms and metastases can be detected.
-
MRI of the pelvis, abdomen and retroperitoneal space;
The main indications for diagnosis:
- tumors of any nature;
- intestinal polyps;
- abdominal trauma;
- inflammatory processes;
- reproductive disorders;
- search for metastases in the lymph nodes, spine;
- preparation for gynecological operations.
An MRI scan of the soft tissues of the abdomen and internal organs is necessary when the following complaints and violations appear:
- suspicion of abdominal tumors;
- abdominal pain of any etiology;
- dysfunction of the gallbladder, ducts, intestines;
- suspicion of the presence of parasitic diseases;
- nausea and vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin.
-
MRI of joints and soft tissues, including angiography of arteries and veins of the extremities;
Indications for MRI of joints:
Due to the anatomical features and increased stress, specialists most often do an MRI of the knee joint. The main indication is injury. The study makes it possible to assess the degree of damage during the course.
MRI of the knee meniscus, plan further medical tactics. The method can be used an unlimited number of times, including before medical or diagnostic arthroscopy. MRI of the hip joint is most often prescribed after injuries, to assess the severity of the damage, when the specialist suspects the presence of a fracture of the head, femoral neck, acetabulum, rupture of ligaments and muscles. The method is used to detect tumor processes, metastases.
MRI of the shoulder joint is used for shoulder injuries, suspected malignant and benign tumors, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Also, the study is used in preparation for surgical treatment and to assess the quality of the treatment.
-
MRI with contrast;
The attending physician or radiologist, after examining the images, may recommend that the patient undergo an MRI with contrast.
MRI with contrast is performed in difficult or controversial cases, the procedure gives the attending physician information to clarify the diagnosis or diagnose a relapse of the disease, determine the size, nature of the pathological process, and help draw up a further treatment program. Any organs and tissues can be examined by the contrasting method, but most often it is used to exclude and clarify the pathological process of the brain and spinal cord, as well as internal organs.
-
Whole body MRI is an effective way to diagnose cancer and detect metastases
Contraindications to MRI
The main contraindications for MRI are:
- The presence of a pacemaker in the body;
- The presence of artificial heart valves;
- The presence of joint endoprostheses;
- Metal osteosynthesis;
- Intraocular metal objects;
- Internal infusion pumps for medications;
- Medical metal products: clips, staples, stents, filters, as well as metal fragments, shavings.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
Medical centers offering MRI services in Belarus:
- LODE
- Medical Center MTZ
- Medical center “Tomography” in Minsk
- Medical center MRI in Minsk AVICENNA
- Ecomedservice
- Medical center «Klavira» Minsk
- Medical center Nordin Minsk



 Back
Back